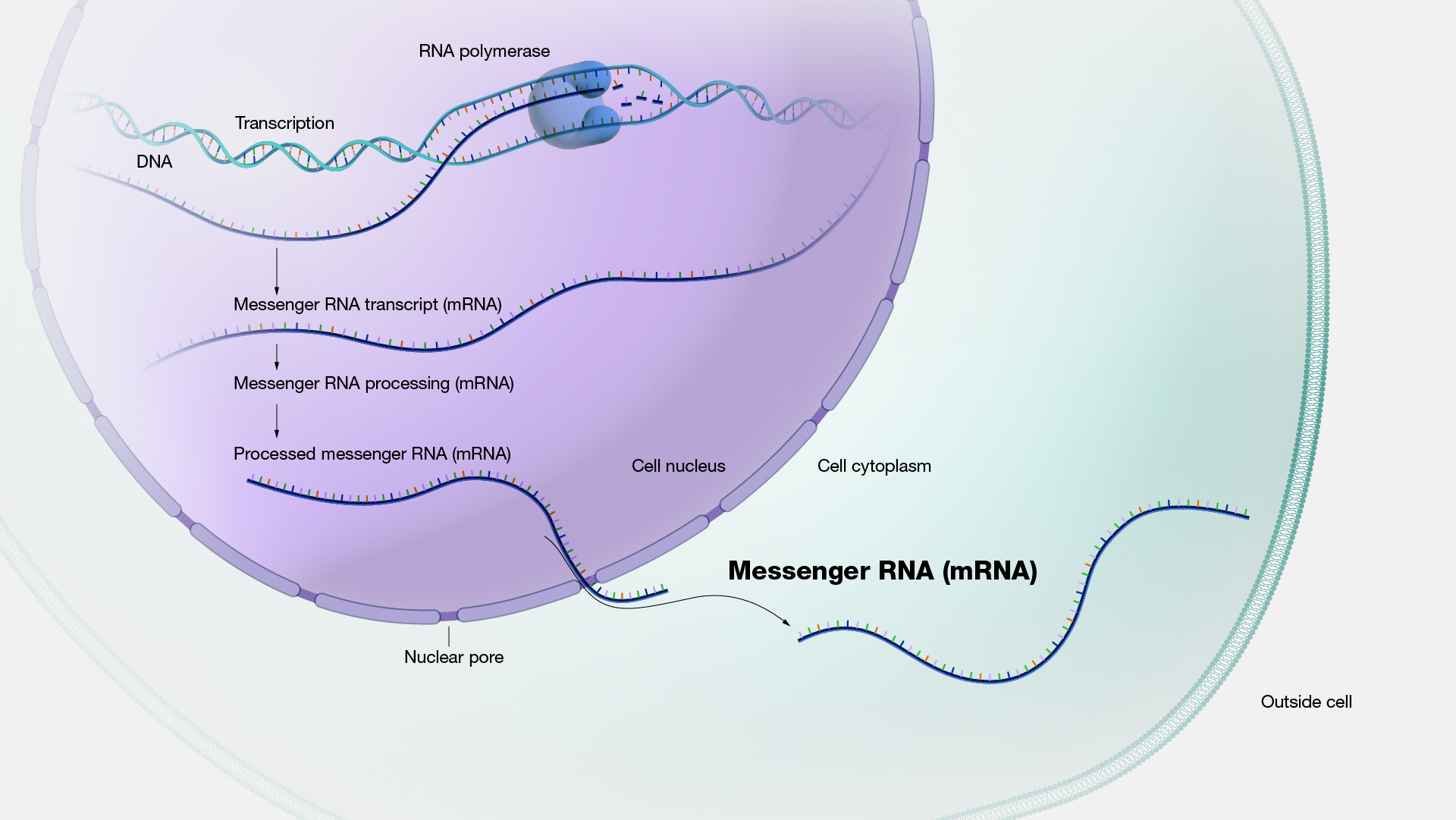
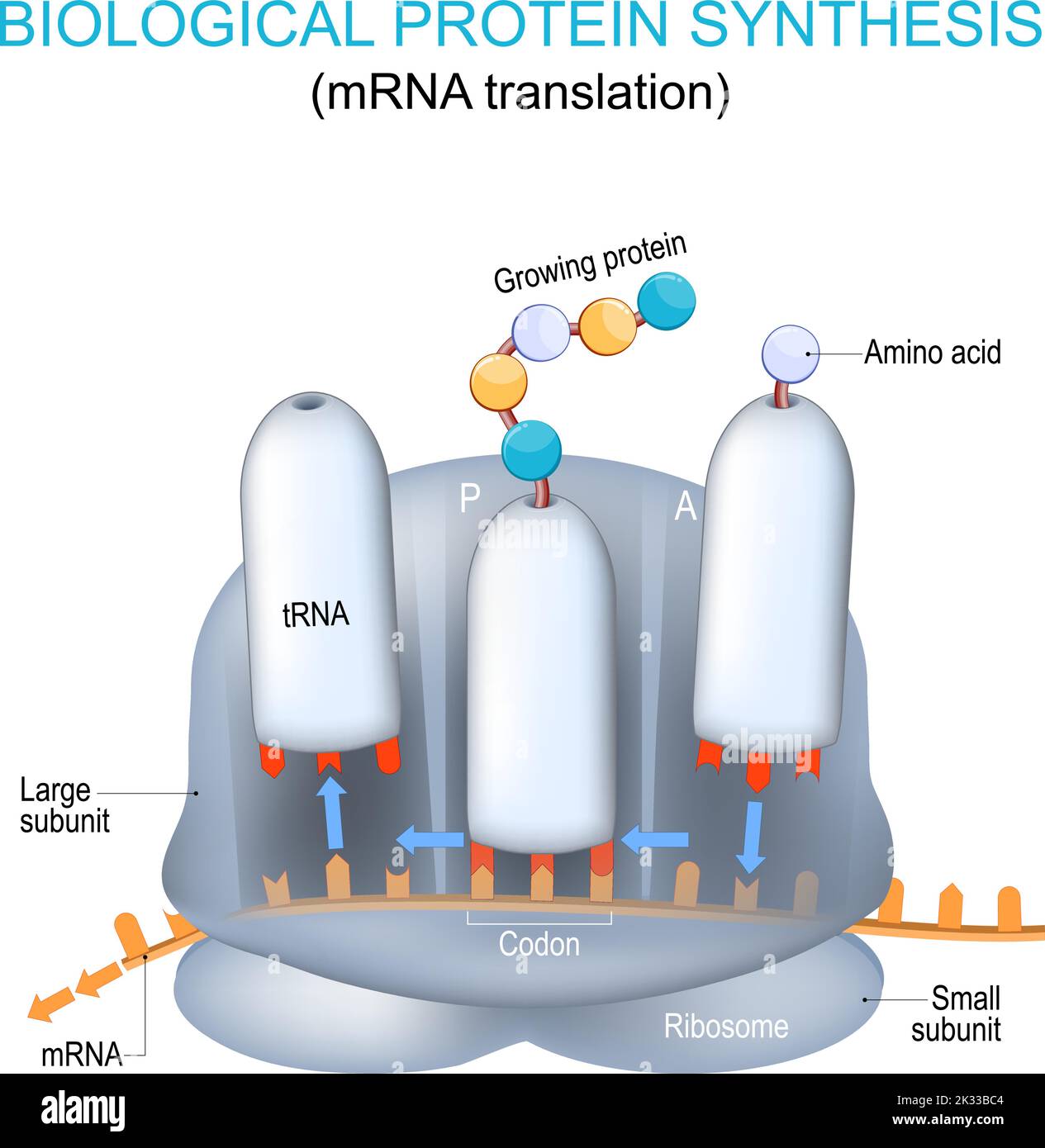
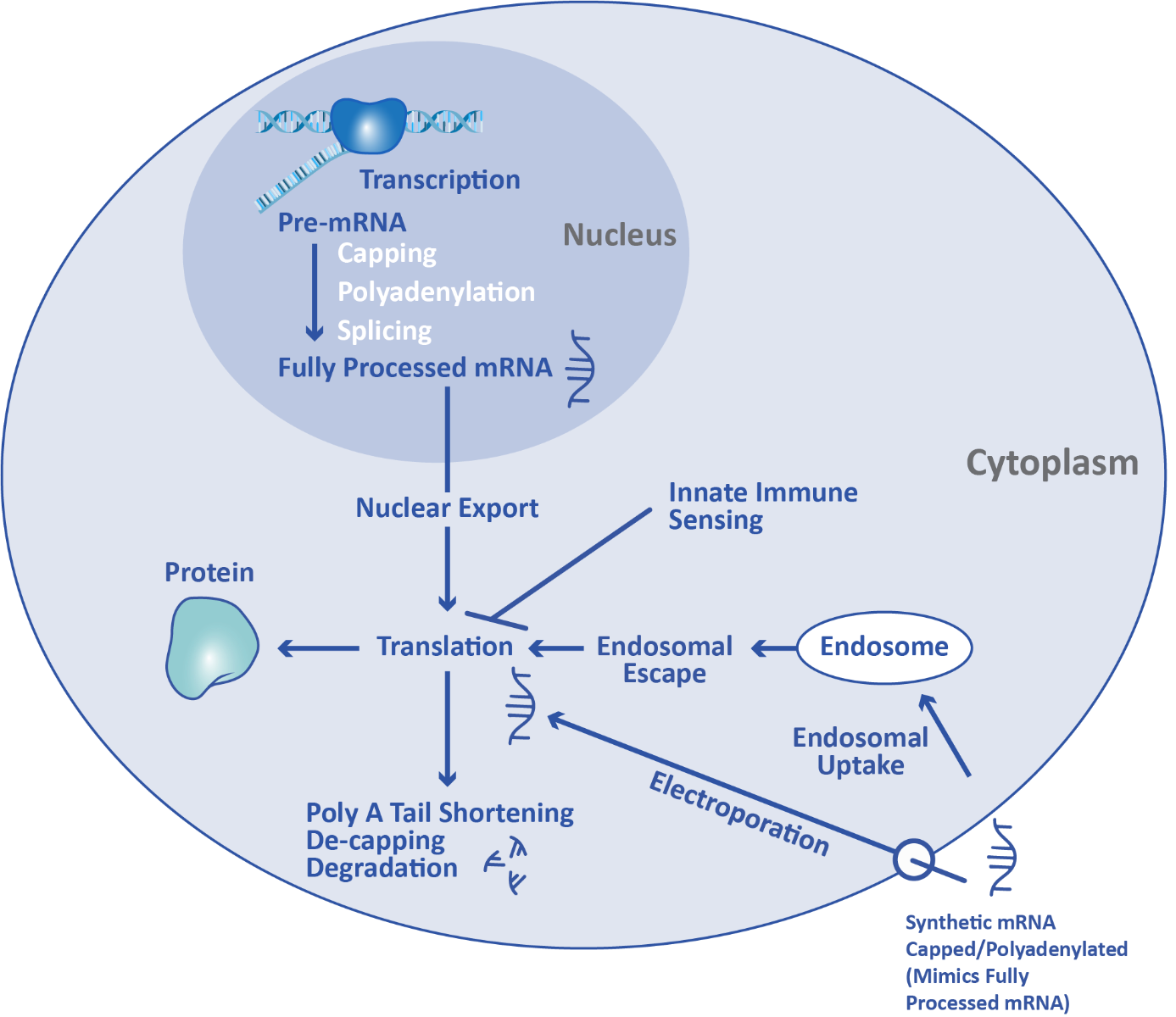
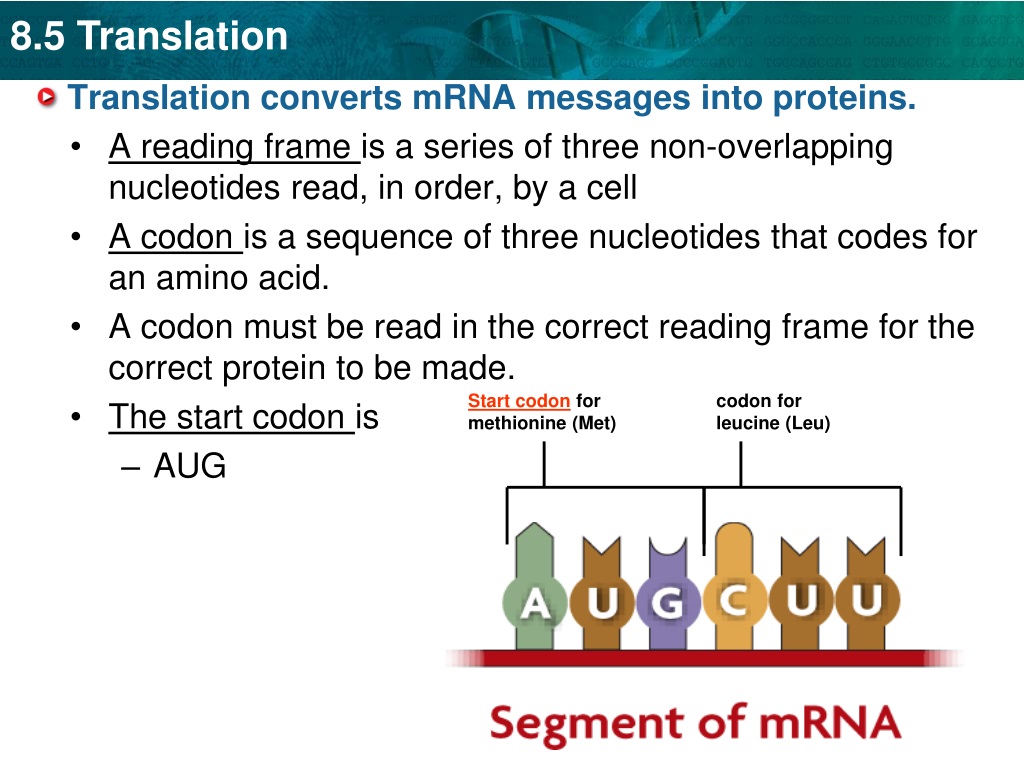
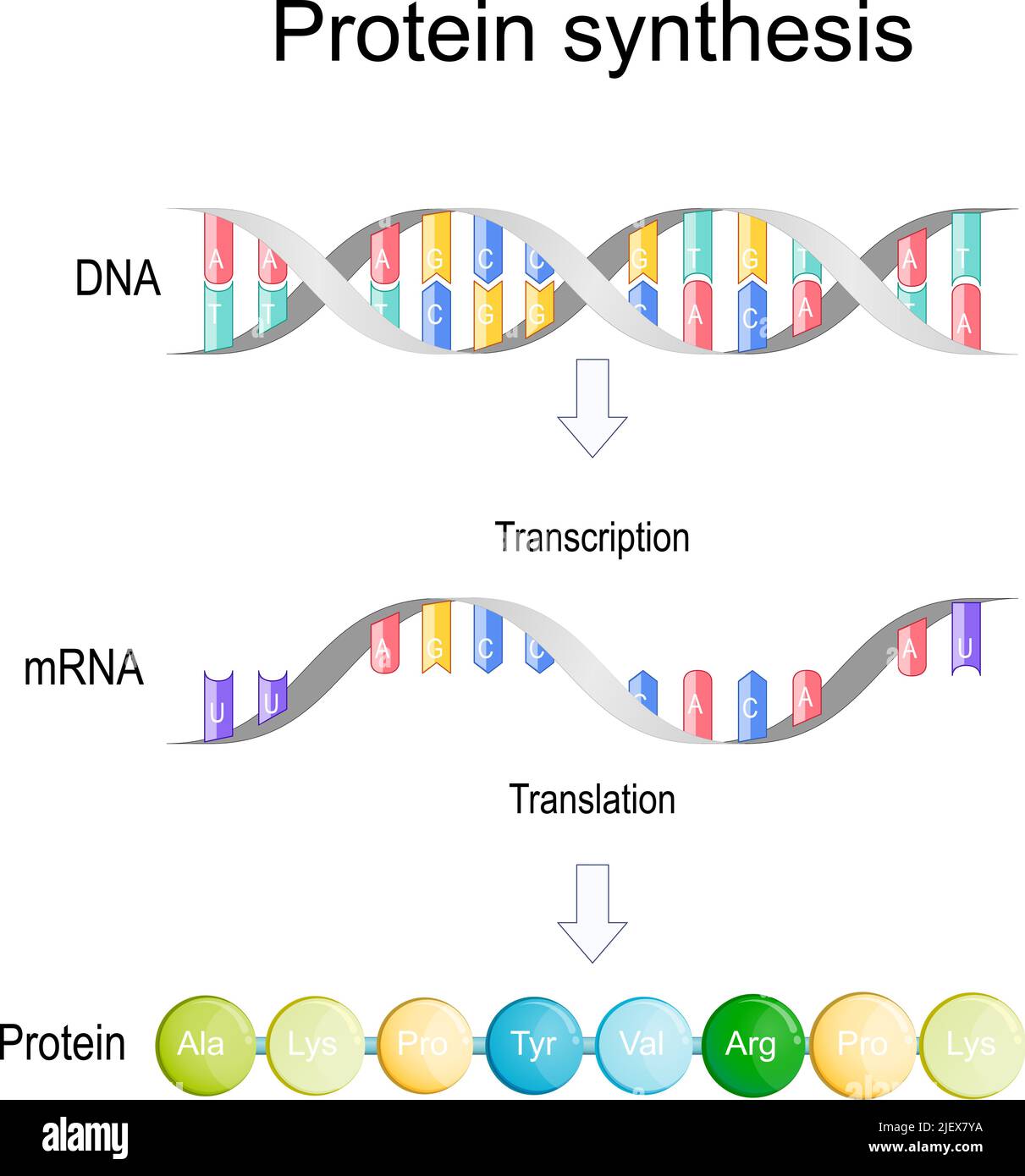
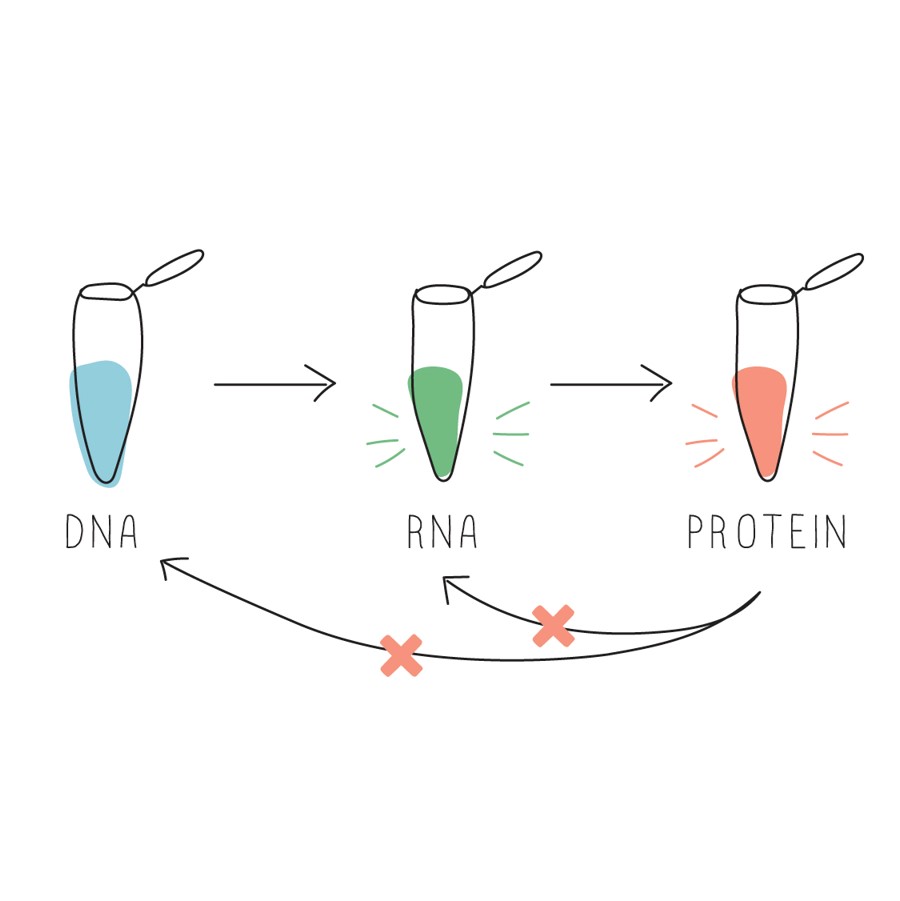
Converts Mrna Into A Protein - Translation converts the genetic information encoded in messenger rna (mrna) into a sequence of amino acids, ultimately. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: In this section we examine. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins. The process in which ribosomes convert mrna into a protein is known as translation. Find out how mrna is read. Learn how the cell converts dna into working proteins through the processes of transcription and translation. This takes place over three main. It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna.
Translation converts the genetic information encoded in messenger rna (mrna) into a sequence of amino acids, ultimately. In this section we examine. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins. Find out how mrna is read. The process in which ribosomes convert mrna into a protein is known as translation. This takes place over three main. It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna. Learn how the cell converts dna into working proteins through the processes of transcription and translation. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology:
It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna. Translation converts the genetic information encoded in messenger rna (mrna) into a sequence of amino acids, ultimately. This takes place over three main. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins. The process in which ribosomes convert mrna into a protein is known as translation. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: Learn how the cell converts dna into working proteins through the processes of transcription and translation. In this section we examine. Find out how mrna is read.
[Solved] 9. The process by which mRNA is converted into a protein
In this section we examine. Find out how mrna is read. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins. This takes place over three main. It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
In this section we examine. Translation converts the genetic information encoded in messenger rna (mrna) into a sequence of amino acids, ultimately. The process in which ribosomes convert mrna into a protein is known as translation. Find out how mrna is read. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology:
Mrna ribosomes Stock Vector Images Alamy
In this section we examine. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: The process in which ribosomes convert mrna into a protein is known as translation. This takes place over three main. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins.
mRNA Basics TriLink BioTechnologies
It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins. Learn how the cell converts dna into working proteins through the processes of transcription and translation. Find out how mrna is read. This takes place over three main.
PPT KEY CONCEPT Translation converts an mRNA message into a protein
Translation converts the genetic information encoded in messenger rna (mrna) into a sequence of amino acids, ultimately. It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna. In this section we examine. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins. Translation is the second part of the central dogma.
Molecule of mRNA, illustration Stock Photo Alamy
In this section we examine. This takes place over three main. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: The process in which ribosomes convert mrna into a protein is known as translation. Translation converts the genetic information encoded in messenger rna (mrna) into a sequence of amino acids, ultimately.
Translation DNA to mRNA to Protein Learn Science at Scitable
Learn how the cell converts dna into working proteins through the processes of transcription and translation. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins. It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna. In this section we examine. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of.
The Role of mRNA in Protein Synthesis Function & Purpose Lesson
Learn how the cell converts dna into working proteins through the processes of transcription and translation. This takes place over three main. It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna. In this section we examine. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins.
Mrna ribosomes Stock Vector Images Alamy
Find out how mrna is read. In this section we examine. This takes place over three main. The process in which ribosomes convert mrna into a protein is known as translation. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins.
Understanding the Science of mRNA Vaccines miniPCR bio
Find out how mrna is read. Learn how the cell converts dna into working proteins through the processes of transcription and translation. It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna. The process in which ribosomes convert mrna into a protein is known as translation. Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology:
Learn How The Cell Converts Dna Into Working Proteins Through The Processes Of Transcription And Translation.
The process in which ribosomes convert mrna into a protein is known as translation. It is the process in which the genetic code in mrna. Find out how mrna is read. Translation converts the genetic information encoded in messenger rna (mrna) into a sequence of amino acids, ultimately.
In This Section We Examine.
Translation is the second part of the central dogma of molecular biology: This takes place over three main. However, most genes in a cell produce mrna molecules that serve as intermediaries on the pathway to proteins.